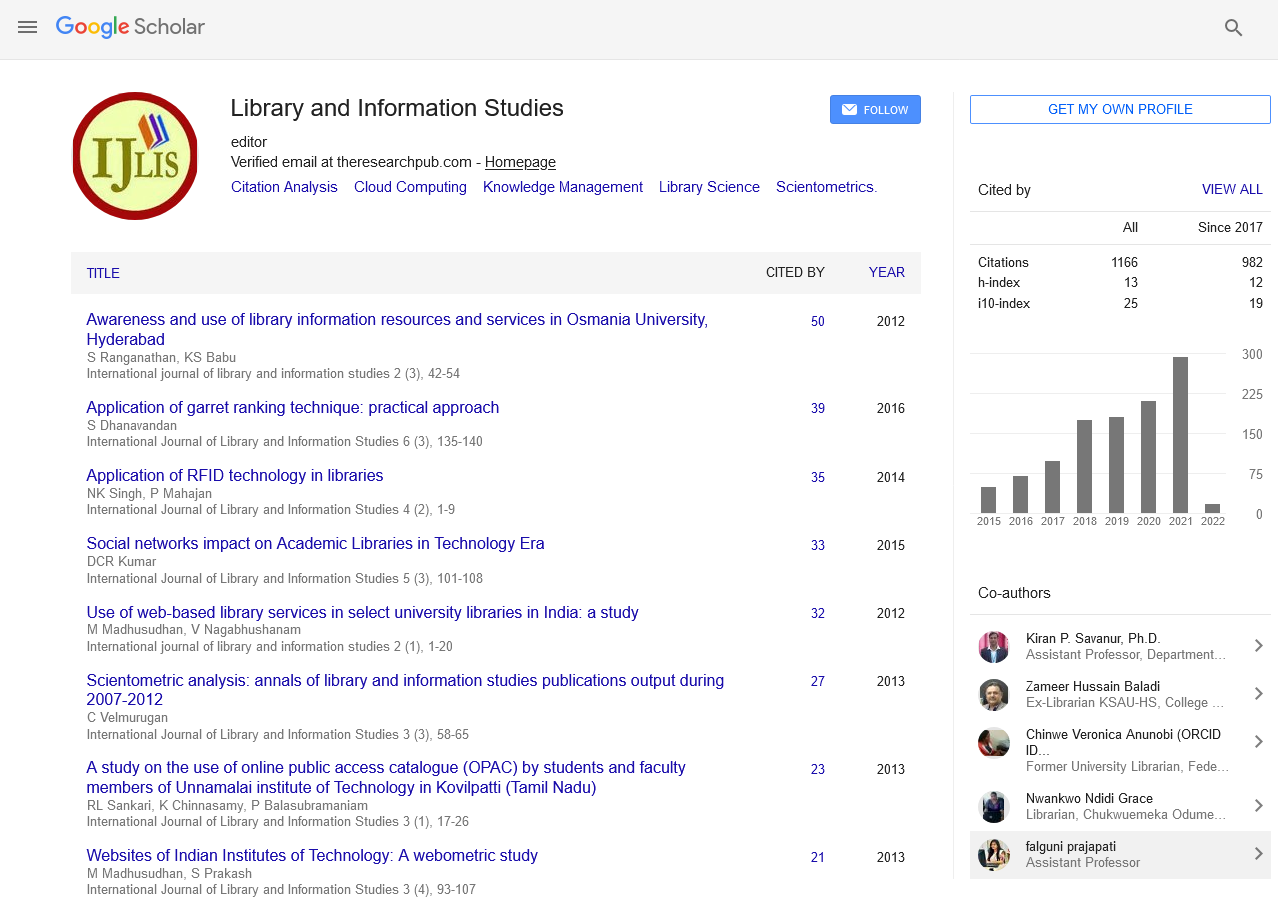
Research Article - (2022) Volume 12, Issue 3
Use of Social Media Engagement Strategies among Librarians during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Osun State, Nigeria
Ajiboye Olubukola*Abstract
The study investigated the use of social media engagement strategies among librarians in Osun State, South-West Nigeria during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Three research questions guided the study. The study adopted a survey research design and online survey form was used as instrument for data collection. The population of the study comprised of professional librarians on the Nigerian Library Association Osun state Chapter and convenience sampling was used. This was largely due to the fact that lockdown banned activities across the states and the only way they could be reached was online. Online forms were distributed in the Nigerian Library Association (NLA) Osun State WhatsApp group and 38 forms were found usable. The study showed that librarians shared content on social media multiple times daily mostly through writing and electronic word-of –mouth activities during the COVID-19 pandemic and this led to increase in audience growth and engagement (likes, shares, mentions, views). The study recommended that librarians should explore more engagement strategies using social media engagement strategies since most of their clienteles reside in the social media.
http://www.surgeryjournals.com/
http://www.surgeryinsights.com/
http://www.medicineinsights.com/
http://www.medicinaljournals.com/
http://www.medicalsci.org/
http://www.eclinjournals.com/
http://www.eclinicalsci.org/
http://www.eclinicaljournals.org/
http://www.eclinicalinsight.com/
http://www.clinicalres.org/
http://www.clinicalinsight.org/
http://www.clinicalmedicaljournal.com/
http://www.clinicalmedicaljournal.org/
http://www.tradescience.org/
http://www.pharmares.org/
http://www.pharmainsights.org/
http://www.epharmajournal.org/
http://www.epharmajournal.com/
http://www.nursingres.org/
http://www.nursingres.com/
http://www.healthcareres.org/
http://www.healthcareinsights.org/
http://www.enursingcentral.com/
http://www.enursingcare.org/
http://www.ehealthjournals.org/
http://www.ehealthjournals.com/
http://www.psychiatryres.com/
http://www.neurologyres.com/
http://www.neurologyinsights.org/
http://www.neurologyinsight.com/
http://www.managjournal.com/
http://www.emedscience.org/
http://www.emedicinejournals.org/
http://www.molbioljournal.org/
http://www.molbioljournal.com/
http://www.engjournals.com/
http://www.enginsights.org/
http://www.edentalcentral.com/
http://www.dentistryjournals.org/
http://www.dentistryinsights.org/
http://www.scitechjournal.org/
http://www.jscitech.com/
http://www.pulsusjournal.com/
http://www.peerreviewjournal.org/
http://www.peerreviewjournal.com/
http://www.peerreviewedjournals.org/
http://www.journalinsight.org/
http://www.escientificjournals.com/
http://www.escienceopen.com/
http://www.esciencejournals.org/
http://www.esciencejournals.com/
http://www.emedicalscience.com/
http://www.emedicalsci.org/
http://www.emedicalsci.com/
http://www.microbiologyres.com/
http://www.microbialjournals.com/
http://www.immunologyres.com/
http://www.immunologyinsights.com/
http://www.molecularbiol.com/
http://www.esciencejournal.org/
Keywords
Social Media, Engagement, Librarians, Users, COVID-19 Pandemic
Introduction
The library and information profession is currently witnessing a significant shift in the mode of information service delivery, particularly in user-librarian communication and interaction. Social media, as a web-based channel of information dissemination, plays an essential role in this shift and is rapidly permeating all aspects of library and information services. It has the potential to facilitate much closer relationships between libraries and their customers-wherever they are based, and however they choose to learn about and access library services and resources (Adewoyin 1). It has provided libraries with new avenues to connect with their users and promote library resources and services beyond the library walls.
In the marketing and public relations context, organizations seek to achieve four main objectives regarding their use of social media which are increasing sales, saving costs, aiming at a higher user satisfaction and improving their reputation and relevance. These objectives have some relevance to the library (Al-Daihani 2). A survey conducted by EBSCO among European libraries suggests that the goals of libraries’ social media involvement are to maximize library exposure, to modernize the library image and e-reputation, to promote specific content offers, to build discussion groups and collaborative work (Amuda and Tella 3). As a feature of Web 2.0, social media offers libraries a new way to connect, engage, and communicate with customers. This means that libraries are leveraging the ubiquity and communication advantages of social media to facilitate the achievement of their goals (Aregbesola, et al. 4).
Statement of problem
The rise in the number of affected cases of COVID-19 in Nigeria necessitated the President of Nigeria, Muhammadu Buhari in his speech, on 30th March 2020, to order a lockdown on the nation’s activities inclusive of libraries in both private and public parastatals. The implication of this lockdown directive was that libraries were physically closed and services were delivered mainly through social media throughout the period of the lockdown (Dessart, et al. 5). In lieu of this, it became pertinent to investigate how librarians engaged and retained their users through social media during the COVID-19 pandemic (Dijkmans, et al. 6).
Objectives
The specific objectives of the study are to:
• Determine the influence of engagement strategies on Social Media metrics among librarians in Osun state during the COVID-19 pandemic
• Determine the commonly used Social media by librarians in Osun State during the COVID-19 pandemic
• Determine the challenges faced by librarians when using Social Media during the COVID-19 pandemic
Materials and Methods
Reported that 86% of libraries make use of social media and the top two social media platforms used by libraries are Facebook 99% and Twitter 56%. Many academic and public libraries in the United States have been embracing the use of web 2.0 and social networking tools to enhance services to library patrons (Emezie and Ngozi 7). Related studies show that librarians use majorly Facebook and social networks to enable libraries to connect, communicate and collaborate between libraries and users. In the same vein, discovered a positive relationship between social media, perceived reputation, customer engagement, return-on-investment, profitability, increased sales, and customer retention. Likewise, discovered that interested customers were more likely to click advertising links, which increased traffic and other business-related activities (Fang, et al. 8).
A study analysed Facebook posts of 100 English-speaking universities as listed by the 2014 Shanghai World University Ranking. It focused on the dataset from a 2-year posting history totalling 18,333 posts, 113,621 likes and 3401 comments (Fernandez 9). Findings revealed that posts with the most engagement were those featuring photos and the use of personal terms such as ‘congratulations’ and ‘thanks’. Similarly, a study investigated whether there was a correlation between Pilipino university libraries’ Facebook posts and the user engagement they generated. It found that while photo and event-related posts gathered a higher level of interaction, engagement was low for the majority of the libraries. The studies under this category are still growing. Hence, further studies are needed to ascertain the underlying factors that may contribute to a better librarian-user social media engagement. Collected data from 433 institutional library accounts: Academic, public, state and national libraries by searching for “library” on Twitter’s search facility. He found that only 30% of the libraries averaged one post per day for the duration of their time on Twitter and 59% of them were following fewer than a hundred other Twitter streams, which according to him suggested inactivity that may not encourage conversations with the users.
Discovered that the major constraints that librarians face in the use of social media for service delivery are erratic power supply, lack of finance and poor internet access. Similarly, revealed that the most challenge to library professionals’ use of social networking sites in universities in Ogun State is lack of social media skills and low bandwidth.
Results and Discussion
The survey research method was used for this study. The population of this study comprised of professional librarians in Osun State. Online survey form was the instrument used for data collection. Convenience sampling technique was employed because as at the time of administration of the research instrument, lockdown activities were totally enforced because of the COVID-19 Pandemic and hence online administration of the instrument was considered most effective. The forms were distributed on the Nigerian Library Association (NLA) Whatsapp chat group, Osun State Chapter (Harrison, et al. 10). Thirty eight online survey forms were found usable for this study which made up the sample size (Table 1).
| Items | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| 25-34 | 4 | 10.5 |
| 35-44 | 20 | 52.6 |
| 45-54 | 9 | 23.7 |
| 55-64 | 5 | 13.2 |
| Total | 38 | 100 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 20 | 52.6 |
| Female | 18 | 47.4 |
| Total | 38 | 100 |
| Social media channel most used | ||
| 24 | 63.2 | |
| 2 | 5.2 | |
| 6 | 15.8 | |
| 1 | 2.6 | |
| 5 | 13.2 | |
| Total | 38 | 100 |
| How often do you share content on social media? | ||
| Multiple times per day | 17 | 44.7 |
| Once a day | 6 | 15.8 |
| Weekly | 3 | 7.9 |
| Monthly | 1 | 2.6 |
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics and use of Social Media Engagement Strategies of Librarians
The demographic characteristics of the respondents show that 52.6% of the respondents are male while 47.4% constituted female. This shows that there is almost an equal distribution between male and female. One may infer that there is almost equal distribution of both male and female librarians in Osun State (Hibbler, et al. 11). A question was asked on the Social Media channel commonly preferred by librarians (Idiegbeyan 12). 24 people 63.2%) chose Facebook, 6 people (15.8%) chose WhatsApp while 5 respondents (13.2%) of the population chose LinkedIn.
A question on how often librarians shared content on Social Media was asked. 13 respondents (34.2%) which has the highest frequency chose multiple times per day, 11(28.9%) chose inconsistently, 6 respondents (15.8%) chose once per day, while 3 respondents (7.9%) chose weekly and 1 respondent chose monthly. The clause of lockdown activities may have given information professionals adequate time to engage more frequently on social media than at other times (Ihejirika, et al. 13).
To determine customer engagement strategies, a question was asked on how librarians engaged customers most on social media (Luo, et al. 14).
Hypothesis H1: There is no significant relationship between customer engagement strategies and Social Media metrics among librarians in Osun State. 23 people (41.8%) with the highest frequency chose writing, 17 respondents (30.9%) chose electronic word-of-mouth activities, 9 respondents (16.4%) chose Product or service reviews while 6 people (10.9%) chose blogging (Nyekwere, et al. 15). When asked about the challenges librarians professionals faced when using social media, internet connectivity had the highest frequency of 26 respondents (26.5%), which was followed by inadequate electricity supply which had a frequency of 22 respondents ( 22.4%), 14 respondents (14.3%) chose Cybercrimes while 13 respondents (13.3%) chose fraudsters (Olajide, et al. 16).
Research question 1: What is the effect of engagement strategies on social media metrics among librarians in Osun State during the COVID-19 pandemic? As often as librarians shared content multiple times daily, there was an impact on user engagement that was evident through increase in audience growth and engagement (likes, shares, mentions, views). This implies that as often as librarians are actively engaged via social media, there is a tendency for corresponding positive effect of customer loyalty and participation (Omini and Kekayo 17). This result corroborates with the findings of which state that effective customer engagement increased brand loyalty and was critical for business survival. Respondents were asked to rate the impact of social media on library services and identify the metrics they used for their ratings. Engagement (likes, shares, mentions, views) which had 34% and audience growth (29.8%) were the metrics that had the highest percentages that were used (Peñaflor 18). The result also showed that librarians shared content on social media multiple times daily mostly through writing and electronic word-of–mouth activities. This finding further corroborates the study of which discovered a positive relationship between social media customer engagement, increased sales, return-on-investment, profitability, perceived reputation, and customer retention (Quadri and Oluwafemi 19).
Research question 2: What is the commonly used social media by librarians for service delivery in Osun State during the COVID-19 pandemic? The findings of the study reveal that 47.4% chose Facebook, 6 respondents (15.8%) chose WhatsApp while 5 respondents (13.2%) of the population chose LinkedIn. This result corroborates with the findings who reported that 86% of libraries make use of Social Media and the top two Social Media platforms used by libraries are Facebook 99% and Twitter 56%. This finding further corroborates with studies that show that librarians use majorly Facebook and social networks enable libraries to connect, communicate and collaborate between libraries and users (Stuart 20).
Research question 3: What are the challenges faced by librarians when using social media in Osun State?
Question on what challenges librarians faced when using social media was asked. Top on the list was poor internet connectivity and inadequate electricity supply with 26.5% and 22.4% respectively (Table 2). This study corroborates that of their study which discovered that the major constraints that librarians face in the use of social media for service delivery are erratic power supply, lack of finance and poor internet access.
| Correlations | Engagement strategies | Social Media metrics |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Engagement strategies | Pearson Correlation |
1 | .451** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | - | 0.004 | |
| N | 38 | 38 | |
| Social Media metrics | Pearson Correlation |
.451** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.004 | - | |
| N | 38 | 38 | |
** Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
Table 2: Correlation Significant
This result showed that there is significant moderate and positive relationship between user engagement and social media metrics which carries a correlation coefficient value of 0.451 and p-value of 0.004 which is significant at the alpha value of 0.01. Thus the null hypothesis was rejected. The finding of this study proved that user engagement and social media metrics are positively related (Ugwu 21). This finding further corroborates the study of which discovered a positive relationship between social media customer engagement, increased sales, return-on-investment, profitability, perceived reputation, and customer retention.
Conclusion
The study showed that there was an increase in the level of engagement with the users of the library which resulted to audience growth. This may have been due to the fact that both librarians and users were at home and had more time for social media use. The study also revealed that the most commonly used social media among librarians in Osun State during the pandemic was Facebook. However, inadequate power supply and poor internet connection were recorded as the major challenges faced by librarians in the use of social media for library services during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Recommendations
In light of the findings from this study, the following recommendations are made:
• Libraries should adopt the use of social media in the delivery of their services
• Librarians should explore more social media engagement strategies like posting videos and pictures that attract more engagement and interest
• Librarians should explore alternative sources of power supply such as solar power to have better access to power supply.
References
- Adewoyin, Omobola Olufunke, et al. "Social media use and service delivery by librarians in federal universities in south-west, Nigeria." Libr Philos Pract (e-journal) 1641 (2017).
- l-Daihani, Sultan M, and Suha A. "Exploring academic libraries’ use of Twitter: a content analysis". Electron Libr (2015).
- Amuda, Halimah Odunayo, and Tella Adeyinka. "Application of social media for innovative library services in South-Western Nigerian University libraries." J Balkan Libr Union 5.2 (2017): 10-16.
- Aregbesola, Ayooluwa, et al. "Infopreneurship in a developing country: Opportunities and Challenges" Mater Sci Eng 640. 1 (2019): 012123. IOP Publishing
- Dessart, Laurence, et al. "Consumer engagement in online brand communities: A social media perspective". J Prod Brand Manag (2015).
- Dijkmans, Corné, et al. "A stage to engage: Social media use and corporate reputation". Tour Manag 47(2015): 58-67.
- Emezie, Nkeiru A, and Ngozi Maria Nwaohiri. "Social network as the enabler for library services: Challenges of Nigerian academic libraries". Qualitative Quantitative Methods Libraries 5. 1 (2017).
- Fang, Eric, et al. "Direct and indirect effects of buyers and sellers on search advertising revenues in business-to-business electronic platforms". J Mark Res 52. 3( 2015): 407-422.
- Gonzalez Fernandez Villavicencio N. "The profitability of libraries using social media". Multicult Educ (2014): 561-566.
- Harrison, Amanda, et al. "Social media use in academic libraries: A phenomenological study". J Acad Librariansh 43.3 (2017): 248-256.
- Hibbler-Britt, et al. "Small business success and social capital: A multi-cultural approach". J Bus Financ Res 10. 1 (2015):156. [Cross Ref]
- Idiegbeyan-Ose, Jerome, et al. "Library professionals and social network sites: Use, relevance and challenges from university libraries in Ogun State, Nigeria"
- Ihejirika, Kingsley T, et al. "Rethinking academic library use of social media for marketing: Management strategies for sustainable user engagement". J Libr Adm 61. 1 (2021): 58-85.
- Luo, Lili, et al. "Marketing via social media: A case study". Libr Hi Tech 31.3 (2013): 455-466.
- Nyekwere, Endwell Onyinye, et al. "An assessment of the use of social media as advertising vehicles in Nigeria: A study of Facebook and Twitter". New Media Soc 21.1 (2014): 1-9.
- Olajide, Adebayo Afolabi, et al. "How libraries are using social media: Nigeria perspective". Int J Digital Library Service 7.3 (2017): 79-94.
- Omini, Emmanuel Ubi, and Kekayo Ayanlade Osuolale. Utilization of social media platforms by librarians for promoting library resources and services in Nigerians’ tertiary institutions in Cross River State. Glob J Educ Res 18.1 (2019): 1-8.
- Penaflor, Janice. "Beyond “likes”: An assessment of user engagement in Facebook among Philippine academic libraries". Libr Manag (2018).
- Quadri, Ganiyu Oluwaseyi, and Oluwafemi Adebayo Idowu. Social media use by librarians for information dissemination in three federal university libraries in Southwest Nigeria. J Libr Inf Serv Distance Learn 10.2 (2016): 30-40.
- Stuart, David. What are libraries doing on Twitter? Online 34. 1 (2010): 45-47.
- Ugwu FN. Evaluation of entrepreneurship awareness and skills among LIS students in universities in South East Nigeria. Libr Philos Pract (2012): 1.
Author Info
Ajiboye Olubukola*Received: 10-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. IJLIS-22-51430; Editor assigned: 13-Jan-2022, Pre QC No. IJLIS-22-51430(PQ); Reviewed: 14-Feb-2022, QC No. IJLIS-22-51430; Revised: 21-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. IJLIS-22-51430(R); Published: 28-Feb-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2231-4911.22.12.837
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Call for Papers
Authors can contribute papers on
What is Your ORCID
Register for the persistent digital identifier that distinguishes you from every other researcher.
Social Bookmarking
Know Your Citation Style
American Psychological Association (APA)
Modern Language Association (MLA)
American Anthropological Association (AAA)
Society for American Archaeology
American Antiquity Citation Style
American Medical Association (AMA)
American Political Science Association(APSA)