Mini Review - (2023) Volume 13, Issue 1
Infodemics: The Role of Librarians in Countering Fake News
Madukwe A*Abstract
This paper explores how the field of librarianship can help counteract the phenomenon of Infodemics, fake news, disinformation and misinformation. Thereby, describing the major characteristics of an infodemic, which involves an abhorrent overflow of junks, typically from unreliable sources and spreads with such fervency that it creates chaos. Thereby, combining an inordinately high volume of information (leading to problems relating to locating the information, storage capacity, ensuring quality, visibility and validity) and rapid output (making it hard to assess its value and lead to a waste of effort). This cumulates to the collateral growth of misinformation, disinformation and Malinformation.
Keywords
Infodemics, Fake News, Misinformation, Disinformation, Malinformation.
Introduction
Fake news or better still disinformation, had over the last years increased exponentially with obvious educational, political and social implications. Librarians has argued that libraries should be at the forefront in educating the general public about this phenomenon. Which are capable of causing grave harm when not properly managed and handled. This is because librarians are in the business of acquiring unique skills in other to help patrons by evaluating all kinds of information in whatever medium the comes. It is also important to note that the study of news media has not been integrated well into traditional curricula, its impact on political and daily decision-making highlights its need to be part of both formal and informal education. Therefore, librarians should seek out opportunities across their community to provide literacy tools to empower library patrons. Through provision of a neutral space for consumption and production of media that serves as an educational haven for news literacy and related literacies (Bundy, 2004).
Literature Review
What is an infodemic
Infodemic is an abhorrent flow of junks, typically from unreliable sources and spreads with such fervency that it creates chaos and anarchy in its wake.
It can also be seen as a spontaneous overflow of information which spontaneous overflow of information which are largely false, untrue, deceptive and misleading especially in situations of national emergencies. According to the Oxford English dictionary, an infodemic is “an excessive amount of information about a problem that is typically unreliable, spreads rapidly, and makes a solution more difficult to achieve”. Infodemic refers to a large increase in the volume of information associated with a specific topic and whose growth can occur exponentially in a short period of time due to a specific incident, such as the current global pandemic. In this situation, misinformation and rumors appear on the scene, along with manipulation of information with doubtful intent. In the information age, this phenomenon is amplified through social networks, spreading farther and faster like a virus.
The concept of infodemic and misinformation
Understanding the characteristics of infodemic is a prerequisite to effective information management (Fernandez-Torres, et al., 2021).
Misinformation
This involves the spread of untrue or false information whether intentionally or unintentionally. During period of national emergencies or in times of crisis people can unintentionally spread misinformation without even knowing that the did so. Misinformation happens often in our day to day lives, e.g. one can see or receive a particular information in social media that affects a particular facets of his live, because of emotions or how favorably or unfavorably such piece of information affects him, he shares the information without fact checking or cross checking such information only to find out later that it is false or wrong information. The big tech giants like Google, Facebook and Twitter have over the years made concerted efforts to curb misinformation because if it is not efficiently handled can be weaponized into disinformation (Fernandez, 2019).
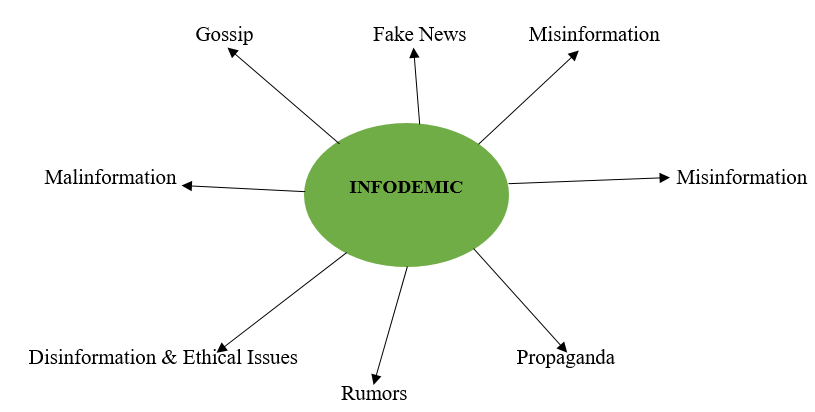
Disinformation and ethical issues: This is the sharing of incorrect information with the intention to harm and create havoc. Thereby, deliberately spreading false and inaccurate information for the sole purpose of misleading and to deceive people into believing stories that are not true about a particular situation. In this era of information explosion misinformation has obvious implication which can adversely affect individual’s mental health. A simple search om a topic on the internet can lead to an exponential overflow of information which, at a first glance can even confuse the searcher or threw him/her off balance. Moreover, in a pandemic scenario misinformation can negatively affect people health. False and misleading stories are concocted, shared or aired without any background check. A greater number of this misinformation are anchored on conspiracy theories, which introduces intriguing elements which if allowed into mainstream discourse should be strongly repudiated (Figure 1).
Malinformation
Occurs when sincere information is circulated to cause damaging consequences either to individual or organization, usually by moving information intended for private consumption into the public domain. Information disorder can lead to fear, anxiety, nervousness and apprehension when it is manipulated to provide distrust or damage to individuals, organizations and governments (De Paor & Bahareh, 2020).
Figure 1: A typical logical framework of an infodemic characteristics.
Discussion
Roles of librarians in curbing infodemic
Information literacy a panacea for fighting infodemics: It is believed that the spread of infodemic is as a result of lack of knowledge or understanding of information literacy. Information literacy is traditionally associated with the field of librarianship to initially emerged from the concept of bibliographic instruction which assisted information consumers with locating and retrieving information. As posited by, one of the competencies expected of persons possessing information literacy is that they can evaluate information and the information-seeking process critically and able to derive satisfaction and personal fulfillment from using information wisely (Biradar, 2022). An information literate person can ascertain the authenticity, usefulness and reliability of the information, by applying some well established and useful evaluative criteria.
Increase transparency and efficiency of fact checking practice There should be a synergy and a collaboration between librarians and the independent fact checkers. Libraries being the store keeper of recorded knowledge should ensure that the fact checkers are provided with the requisite information and knowledge in the course of carrying out their activities (Naeem & Rubina, 2020).
Narrow down ways of tracking rumors and listen to community gist As librarians it is pertinent and necessary to understand the latest gist and information that is being discussed in your community. This will help to foster a better understanding of what is being discussed and the newest trend in town. If it is a propaganda the librarians can help diffuse the situation (Bangani, 2021).
Dialogue with your community to understand their information needs You can run a questionnaire or an online survey in order to build and develop a relationship with the user community. Understanding the information needs of your community enables you to be better prepared and proactive.
Conclusion
After critically analyzing and reviewing infodemics: The roles of librarians in countering fake news insightful conclusions were identified. From the original academic standpoint of fake news this represents a major challenge to libraries and librarians. In period of uncertainty and information explosion, it rests on the librarians to explore opportunities to meet the information needs of core and new audiences and to stay focused on accessibility and readability when vetting information materials. The ability to address any infodemic depends upon the librarian ability to state and curate trustworthy, evidence-based knowledge resources that benefit all of the patrons involved in the pandemic information life cycle. Clearly, there is a strong need to develop and broaden information literacy strategies and methods, as well as to seek other ways of fighting against fake news.
References
- Bundy, Alan. "Australian and New Zealand information literacy framework." Principle Standard Pract 2 (2004): 47-48.
- Fernandez-Torres, Maria Jesus, et al. "Infodemic and fake news in Spain during the COVID-19 pandemic." Int J Environ Res Public Health 18.4 (2021): 1780-1781.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, Leticia Rodriguez. "Desinformacion y comunicacion organizacional: Estudio sobre el impacto de las fake news." Revista Latina Comun Social 74 (2019): 1714-1728.
- De Paor, Saoirse, and Bahareh Heravi. "Information literacy and fake news: How the field of librarianship can help combat the epidemic of fake news." J Acad Librarianship 46.5 (2020): 102218.
- Biradar, Shankar, et al. "Combating the infodemic: COVID-19 induced fake news recognition in social media networks." Complex Intell Systems (2022): 1-13.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naeem, Salman Bin and Rubina Bhatti. "The COVID‐19 infodemi: A new front for information professionals." Health Info Libr J 37.3 (2020): 233-239.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bangani, Siviwe. "The fake news wave: Academic libraries' battle against misinformation during COVID-19." J Acad Librarianship 47.5 (2021): 102390.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Author Info
Madukwe A*Received: 01-Jul-2021, Manuscript No. IJLIS-21-35199; Editor assigned: 06-Jul-2021, Pre QC No. IJLIS-21-35199; Reviewed: 20-Jul-2021, QC No. IJLIS-21-35199; Revised: 01-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. IJLIS-21-35199; Published: 28-Feb-2023, DOI: 10.35248/2231- 4911.23.13.839
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Call for Papers
Authors can contribute papers on
What is Your ORCID
Register for the persistent digital identifier that distinguishes you from every other researcher.
Social Bookmarking
Know Your Citation Style
American Psychological Association (APA)
Modern Language Association (MLA)
American Anthropological Association (AAA)
Society for American Archaeology
American Antiquity Citation Style
American Medical Association (AMA)
American Political Science Association(APSA)