Review Article - (2024) Volume 14, Issue 1
A Review of Cloud Computing and Applications to Academic Library
Omole Victoria Imabong*Abstract
In the history of services, cloud computing is a new phenomenon which is offered over the internet. The technology has brought significant advances in the Information Technology (IT) domain. The study provides a review of cloud computing with its application to academic libraries. The biggest benefit for Libraries is that it offers services using hardware or software or platform of third party sources. It is very economical as it saves cost and maintenance.
This paper attempts to establish a review of cloud computing and applications to academic library. This paper discusses about the meaning of clouds, review cloud computing, gave a universal definition given by NIST(National Institute of Standards and Technology) on cloud computing ,five essential elements of cloud computing , types, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, its application to academic libraries, use of technology, initiatives of cloud computing.
Conclusively, cloud computing technology has provided libraries opportunities for improving their services and making them relevant in today’s information society.
Keywords
Clouds, Cloud computing, Libraries, Academic libraries
Introduction
The new era of technological trend has enabled the discovery of a new computing model known as cloud computing which involves resources (e.g., CPU and storage) being provided as general utilities that can be leased and released by users through the Internet in an on-demand fashion. It has emerged as a buzz word in the distributed computing community. So it will be necessary to define cloud computing, look at the models of cloud computing, challenges and issues in cloud computing.
Libraries are using computers for running services such as Integrated Library Management Software (ILMS), website or portal, digital library or institutional repository, etc. These are either maintained by parent organization’s computer staff or library staff. It involves investment on hardware, software, and staff to maintain these services and undertake backup and upgrade as when new version of the software gets released. Library professionals in most cases are not being trained in maintaining servers, find it difficult to undertake some of these activities without the support of IT staff from within or outside the organization. Now cloud computing has become a new buzzword in the field of libraries, which is blessing in disguise to run different ICT services without much of a problem as third-party services will manage servers and undertake upgrades and take backup of data.
For further clarification of terms, I aim to define key research issues and articulate future research challenges and directions for cloud computing. To this end, the following will be discussed; cloud, cloud computing, characteristics of cloud computing, cloud computing service models, advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing, academic libraries, application of cloud computing to academic libraries to mention but few.
Literature Review
What is cloud?
According to Lewis, the word cloud is used as a metaphor for the internet. It is based on the standardized use of a cloudlike shape to denote a network on telephony schematics and later to depict the Internet in computer network diagrams as an abstraction of the underlying infrastructure it represents [1].
It refers to servers that are accessed over the internet and the software and databases that run on those servers. That is, network or internet. Services can be provided using network, i.e., on public networks or on private networks (WAN, LAN or VPN) through the cloud. Applications such as e-mail, web conferencing, customer relationship management all run in cloud. It enables users to access the same files and applications from any devices due to computing and storage that takes place on servers in a data centre.
Review of cloud computing
Cloud computing lacks standard definition which has generated not only market hypes, but also, a fair amount of skepticism and confusion. Various definitions and interpretations for cloud computing shall be examined.
According to Lewis G., “Cloud” element of cloud computing can be seen as an acronym that stands for:
C: Stands for computing resources.
L: Stands for location independent.
O: Can be accessed via online means.
U: Used as a utility.
D: Is available on demand.
Cloud computing can be simply defined as a new style of computing in which dynamically scalable and often virtualized resources are provided as a services over the internet. That is, it is the use of internet for computing needs. According to Wikipedia, cloud computing is “the delivery of computing as a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software, and information are provided to computers and other devices as a metered service over a network, typically the internet” [2].
For further simplification, Scale, M.S. defines cloud computing as “the sharing and using of applications and resources of a network environment to get work done without concern about ownership and management of the network’s resources and applications” [3]. Gartner Group defined cloud computing as “a style of computing in which massively scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are delivered as a service to external customers using internet technologies.” [4]. While Forrester defines cloud computing as “A pool of abstracted, highly scalable, and managed compute infrastructure capable of hosting end-customer applications and billed by consumption” [5].
A definition was also given by Buyya. He defined cloud computing as:
• A parallel and distributed computing system.
• Consisting of a collection of inter-connected and virtualized computers.
• They are dynamically provisioned and presented as one or more unified
computing resources.
• Are based on Service Level Agreements (SLA) established through negotiation
between the service provider and consumers [6].
In order to have a universally acceptable definition, a definition was given by U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). They defined cloud computing as” a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g. networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models” [7]. This simply means that cloud computing is a network computing model that relies on distributed systems to deliver computing services on demand. Cloud computing facilitates remote access to robust computing process rather than requiring local infrastructure and expertise to configure and merge hardware. This definition includes cloud architectures, security, and deployment strategies.
In particular, five essential elements of cloud computing is clearly identified. They are as follows:
• On-demand self-service: This ensures computing capabilities, without having
engineers for peak loads. That is, consumers provides computing capabilities, such as
server time and network storage, without requiring human interaction with each service
provider.
• Broad network access: Computing capabilities are available over the network (e.g.
internet) and can be accessed through any standardized mechanism which promotes use
by heterogeneous platforms (such as mobile phones, laptops, and PDAs) situated at a
consumer's site.
• Resource pooling: This involves multi-tenancy. That is, cloud service providers pool
their resources that are then shared by multiple users. For example a physical server
may host several virtual machines belonging to different users on demand, resulting in
cost savings to the user. Customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact
location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level
of abstraction (e.g., country, state, or data centre) due to the sense of location
independence. Examples of resources include storage, processing, memory, and
network bandwidth.
• Rapid elasticity: A user can quickly acquire more resources from the cloud by scaling
out and also scale back by releasing those resources once they are no longer required.
The capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be
appropriated in any quantity at any time to the consumers.
• Measured service: Cloud infrastructure is able to use appropriate mechanisms in
measuring the usage of the resources for each individual consumer through its metering
capability despite the fact that computing resources are pooled and shared by multiple
consumers (i.e. multi-tenancy) [8].
Types of cloud computing
Cloud Computing can be broadly divided into two. They are:
• On the basis of service
• On the basis of usage
On the basis of service
• Infrastructure: This is a typical resource cloud computing. It is provided by third
party as a service to users to use them the way they want. An example is the amazon
simple storage service (Amazon S3).
• Platform: It is a set of computer application developed and hosted on the cloud to
access and manage the data. Here, the cloud providers deliver a computing platform
typically including operating system, programming language execution environment,
database, and web server. For example: Google app Engine, Windows Azure
(platform).
• Services: They are the set of applications developed by the service provider to use both
the cloud infrastructure and platform. For example: Google Docs
On the basis of usage
• Private clouds: They are available only to the members of the organization. They
facilitate user to store and disseminate their data on respective cloud. It offers the
highest degree of control over performance, reliability and security. However, they are
often criticized for being similar to traditional proprietary server farms and do not
provide benefits such as no up-front capital costs. They are also known as internal
clouds. For example: Institutional cloud, ebay etc.
• Public clouds: This involves an organisation using cloud service from third party
which may be available for free or with cost. It lacks fine-grained control over data,
network and security settings, which hampers their effectiveness in many business
scenarios. Examples are Google apps, Windows Azure.
• Hybrid clouds: This is a combination of public and private cloud models .This tries to
address the limitations of each approach. In this type of cloud, part of the service
infrastructure runs in private clouds while the remaining part runs in public clouds.
This is more flexible in nature than both public and private clouds. They also provide
tighter control and security over application data compared to public clouds, while still
facilitating on-demand service expansion and contraction. The only disadvantage is
that, designing a hybrid cloud requires carefully determining the best split between
public and private cloud components.
• Special clouds: They are extensions of normal cloud system that provides additional
services. For example: Google app engine.
• Community clouds: This involves several organizations jointly constructing and
sharing the same cloud infrastructure as well as policies, requirements, values, and
concerns. That is, they are specifically organized clouds and are limited for specific
group. The cloud community forms into a degree of economic scalability and
democratic equilibrium. E.g Institutional Gmail of Google apps (Figure 1).
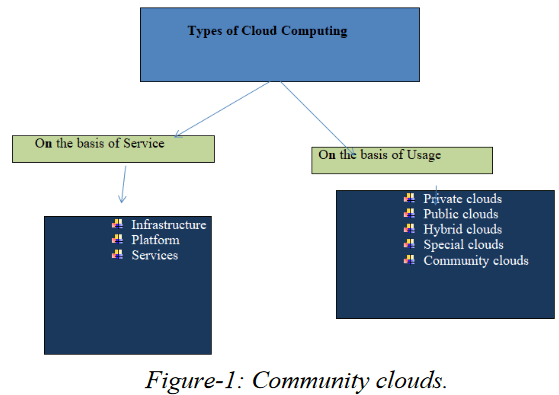
Figure-1: Community clouds.
Characteristics of cloud computing
According to Wang et al., cloud computing has the following number of features compared to other computing paradigms. They are as follows:
• Scalability and on-demand services: Cloud computing provides resources and services
for users on demand. The resources are scalable over several data centres. That is,
scalability and availability issues cause clients to break these agreements.
• User-centric interface: Cloud interfaces are location independent and can be accessed
by well-established interfaces such as Web services and Internet browsers.
• Guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS): Cloud computing guarantees QoS for users in
terms of hardware/CPU performance, bandwidth, and memory capacity.
• Autonomous system: The cloud computing systems are autonomous systems managed
transparently to users. However, software and data inside clouds can be automatically
reconfigured and consolidated to a simple platform depending on user’s needs.
• Pricing: Cloud computing does not require up-from investment. No capital expenditure
is required. Users pay for services and capacity as they need them.
Cloud computing services
Services are provided by cloud computing providers through three (3) basic fundamental models. They are as follows:
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This provides basic storage and computing
capabilities as standardized services over the network. Servers, storage systems,
networking equipment, data centre space etc. are pooled and made available to handle
workloads. The customer would typically deploy his own software on the
infrastructure. Some common examples are Amazon, GoGrid, 3 Tera, etc.
• Software as a Service (SaaS): This Involves cloud providers installing and operating
application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software from cloud
clients. Its elasticity makes this cloud application different from other applications.
This is achieved by cloning tasks onto multiple virtual machines at run-time to meet the
changing work demand. Software as a service only runs software developed by its
vendors according to NIST. SaaS services can be accessed using user interfaces, such
as web browsers via stationary and mobile devices.
• Platform as a Service (PaaS): This service enables the deployment of customized and
acquired applications using tools and programming languages developed by the
provider. It offers services, such as device integration, sandboxes, testing and
instrumentation, session, content, and knowledge management. That is, the enterprises
are helped in building, testing and deploying web based applications. The organisations
do not need to invest for the infrastructure they require for building web and mobile
applications but they have to simply rent, the use of platforms of vendors such as
Windows Azure, Google AppEngine, and Force.com. This service is like water and
electricity facility, where the users have to simply ‘’tap in’’ and take what they need
without worrying about the complexity. It is based on subscription model. Users only
pay for what they use. Users can focus on innovation instead of complex infrastructure.
Libraries and cloud computing
We are living in the information era. Information technology plays a very vital role in handing library resources which ranges from collection, storage, organization, processing, and analysis of information dissemination and so on. Librarians are facing many challenges in the profession due to applications of information technology. In order to satisfy the needs of the knowledge society, new concepts and technologies are being added to ease the practices in the libraries. The emergence of digital library, internet usage, web tools application for libraries, consortium practices leads to the advancement in library profession.
Cloud computing is a completely new IT technology and it is known as the third revolution after PC and internet in IT. The later technology trend in library science is the use of cloud computing for various purposes and for achieving economy in library functions. Since cloud computing is a new and core area, professionals should be aware of it and also the application of cloud computing in library science. Libraries are now moving towards cloud computing technology in present time and taking advantages of cloud based services especially in digital libraries, social networking and information communication. Therefore, it is time for libraries think seriously for libraries services with cloud based technologies and provide reliable and rapid services to their users.
Application of cloud computing in academic libraries
In order to access its services anywhere and anytime, libraries are now shifting their services with the attachment of cloud and networking with the facilities. Libraries are using computers for running services such as Integrated Library Management Software (ILMS), website or portal, digital library or institutional repository, etc. These are either maintained by parent organisation’s computer staff or library staff. It involves investment on hardware, software, and staff to maintain these services and undertake backup and upgrade as and when new version of the software gets released. Cloud based services provide a means for libraries to free resources on information technologies and focus on libraries core competencies-manage, organize and disseminate information.
The following are the possible areas where cloud computing services and applications may be applied:
• Information literacy/orientation: Libraries conduct information literacy and
orientation courses on the cloud. They can keep the tutorials, videos, presentations and
files on the cloud for user’s orientation.
• Building digital library/repositories: Every library develops digital library software.
Cloud computing software help libraries to build an effective and efficient digital
library and digital repositories. An example is the Dura space cloud based digital
library software which is having two software’s namely D-space and Fedora Commons
acts as a complete solution for developing digital libraries/repositories with standard
interfaces and open source codes for the both software.
• Union/shared catalogue/OPAC: Here network libraries use the same platform and
gives access to their collection on one platform. Through cloud computing creation of
union catalogue becomes very easy.
• Collection development: Cloud computing is also used for collection development.
Duplications can be easily avoided and alternate resources can be located and made
accessible to patrons.
• Cataloguing and classification: Cloud computing can also help in the area of
cataloguing and classification by searching the clouds through KOHA for the books
and classify them. For example: Polaris provides variant cloud based services such as
acquisitions, cataloguing, process system, digital contents and provision for inclusion
of cutting edge technologies used in libraries.
• Document download service: Downloading of documents is also ease if there is
permission of access in the network.
• Searching scholarly content: To share various files in electronic form become easy with the cloud computing. Cloud computing facilitates platform to discover and share
the scholarly content. It acts as collaborative platform to empower libraries for dynamic
searching and also for single point search interface, maximizes the usage of all e-resources, customized search across selected sources reduces noise and highlights
relevant content and tools to support the complete research lifecycle.
• E-Learning: cloud computing is boon in the E-Learning environment too. Study
materials are kept on the cloud for reference purpose. Online examinations also can be
conducted. Discussions, revisions can be done at a time from different places. This was
done during COVID-19 era.
• Searching library data: Cloud computing technology also facilitates libraries for
searching and sharing its data for years together. OCLC world cat service has being one
of the popular services for searching library data using cloud computing technology.
OCLC offers various library activities pertaining to circulation, cataloguing, acquisition
and other library related services on cloud platform through the web share management
system.
• Social interactions with the users: social interaction can be possible also through
cloud computing.
• Digital preservation/scanning service: Digitization and scanning work is done
centrally so as to avoid duplication and time consuming work. Libraries can preserve
the collection in digital form in the form of archives.
Cloud computing initiatives for libraries
The following are some of the cloud computing initiatives for libraries:
• Duraspace cloud: This provides open source repository solutions by undertaking
turnkey projects for organizations and libraries to enable them to share scholarly
literature using D-space and fedora commons. Its new service Dura cloud provides
digital preservation support services in the cloud, which is cost effective and simple for
libraries. It also helps libraries to move content to the cloud and store it with different
service providers to eliminate the risk of data loss. The cloud solutions offers include
online backup, preservation and archives, media access and online sharing.
• OCLC webscale: OCLC set an example for other cloud computing in libraries. Years
back OCLC has been functioning as a cloud computing vendor because they provide
cataloguing tools over the internet and allow member institutions to draw on their
centralised data store. It has implemented the plan of library management systems i.e.
Worldshare Management Services (WMS). It has services for many areas in the library
such as acquisitions, analytics, and resource sharing, cataloguing and license
management components. It offers the entire library collection management in a cloud
based application. It also has some certain features that work together to provide its
users better library services and generates cost benefits for libraries and efficiencies not
possibly when utilizing disparate, specialised systems. The service promises to include
privacy, security, scalability and technical support.
• Ex-Libris cloud: It is a leading provider of cloud-based solutions that automate library
operations. In order to create a unified platform for both the management and discovery
of library resources, over 5300 customers in more than 80 countries, including 175 of
top 250 universities worldwide and over 40 national libraries deploy Ex-Libris
solutions. This cloud-based solution allow libraries to lower operational costs, enhance
efficiency, and extend their value to the organization through diverse new services and
collaboration with other libraries and organizations. It also provides streamlined access
to all the library’s collections-whether online journals, e-books, printed resources or
digital material.
• OSS (Open Source Software) labs: Owing to the various capabilities of Amazon such as high durability of data, strong information security based on ISO standards,
scalability, and flexibility, OSS labs from India is using Amazon’s elastic cloud
computing platform. It is expected that the OSS labs will be able to provide robust
open based solutions to demanding customers. Using Amazon’s cloud services, it is
offering Koha, ILS and DSpace institutional repository hosting and software
maintenance subscription services for libraries.
Discussion
Advantages of cloud computing in libraries
The following are some of the advantages of cloud computing in the library:
• Cost saving: In cloud computing, library only pays for those services which he
chooses and this enables the libraries to save on costs. That is, cloud computing
technology is paid incrementally.
• Easy on installation and maintenance: Libraries does not need to worry about
constant server updates and other computing issues.
• Automation: With the help of cloud computing technology, every software update or
maintenance is done automatically by the service provider and the IT or library staff.
• Increased storage: Cloud can hold more storage than a personal computer or the
servers available in the libraries and it is possible to extend as per the need.
• Flexibility: For requesting for an additional space on the servers, cloud computing
technology offers more flexibility to libraries to expand the services anytime and any
day.
• Shared resources: This is the main and important feature of cloud computing that
participating libraries can share their resources. This is known as consortium. By
sharing their resources, they can save on costs and more libraries can access more
number of resources at one place.
• Better mobility: Rather than having to remain present at their desks with a PC and
internet connection, users can access the library servers from wherever they are.
Disadvantages
• Network connectivity and bandwidth: Since the cloud computing is offered over the
Internet, if the connection goes down due to any reason, then the libraries suffer from
loss of data connectivity till the time it is set. Also the service requires more bandwidth,
as it may not work on low speed internet connection.
• Data security and privacy: This is the biggest challenge in cloud computing. If proper
security model is not put in place, then the data stored on the cloud is vulnerable to
attacks from viruses, theft, etc. Also, services offered over the internet are very difficult
to access, the physical location of servers and software and security audit is hard to
undertake. Also, there is a risk of data loss owing to improper backup and systems
failure.
• Dependence on outside agencies: It is virtually difficult to have any control on the
maintenance levels and the frequency since cloud services is being offered by third
party services over the internet. Also it is tough to access the contingency procedures of
the service provider in regard to backup, updates, restore and disaster recovery.
Another issue is the migration to other service provider, if the uniform standards are
not followed by the host.
Conclusion
In conclusion it can be said that cloud computing technology provides libraries an opportunity to improve their services and relevance in today’s information society. It can bring several benefits for libraries and give them a different future. It helps libraries to deliver its resources, services and expertise at the point of need, within user workflows and in a manner that users want and understand. It should free libraries from managing technology so they can focus on collection building, improved services and innovation. The cloud computing model will encourage libraries and their users to participate in a network and community of libraries by enabling them to reuse information and socialize around information. It can also create a powerful, unified presence for libraries on the web and give users a local, group and global.
References
- Scale, M.S.E. "Cloud computing and collaboration." Library Hi Tech News 26.9 (2009): 10-13.
- Buyya R, et al. "Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms: Vision, hype, and reality for delivering computing as the 5th utility." Future Generation computer systems 25.6 (2009): 599-616.
- Wang L, et al. "Scientific cloud computing: Early definition and experience." 2008 10th IEEE International conference on High Performance Computing and Communications. 25-27 September 2008, Dalian, China, 2008.
- Dhamdhere S, and Lihitkar R. "Information common and emerging cloud library technologies." Int Lib Inf Sci 5.10 (2013): 410-416.
- Kaushik, A, and Kumar A. "Application of cloud computing in libraries." J Sci Diss Technol. Res. 3.4 (2013): 270.
- Goldner M, and Birch K. "Resource sharing in a cloud computing age." Interlending and Document Supply 40.1 (2012): 4-11.
- Langmead Ben, and Abhinav Nellore. "Cloud computing for genomic data analysis and collaboration." Nature Reviews Genetics 19.4 (2018): 208-219.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Samarraie H, and Saeed N. "A systematic review of cloud computing tools for collaborative learning: Opportunities and challenges to the blended learning environment." Computers and Education 124 (2018): 77-91.
Author Info
Omole Victoria Imabong*Received: 26-Jun-2023, Manuscript No. IJLIS-23-103932; Editor assigned: 28-Jun-2023, Pre QC No. IJLIS-23-103932 (PQ); Reviewed: 12-Jul-2023, QC No. IJLIS-23-103932; Revised: 03-Jan-2024, Manuscript No. IJLIS-23-103932 (R); Published: 10-Jan-2024, DOI: 10.35248/2231-4911.24.14.856
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Call for Papers
Authors can contribute papers on
What is Your ORCID
Register for the persistent digital identifier that distinguishes you from every other researcher.
Social Bookmarking
Know Your Citation Style
American Psychological Association (APA)
Modern Language Association (MLA)
American Anthropological Association (AAA)
Society for American Archaeology
American Antiquity Citation Style
American Medical Association (AMA)
American Political Science Association(APSA)